The Yagi antenna, also known as the Yagi-Uda antenna, is one of the most popular directional antennas used in various communication systems today. Its simple yet effective design makes it a go-to solution for enhancing signal strength in specific directions. This article explores the structure, benefits, applications, and variations of the Yagi antenna, including insights into directional Yagi antennas.
Table of Contents
What is a Yagi Antenna?
A Yagi antenna is a directional antenna that consists of multiple parallel elements, typically made of metal rods. These elements are aligned along a single axis and serve distinct purposes. The antenna is named after its inventors, Shintaro Uda and Hidetsugu Yagi, who developed the design in the 1920s. Yagi antennas are known for their high directivity, meaning they focus energy in one direction, which makes them ideal for applications where targeted communication is necessary.
Structure of a Yagi Antenna
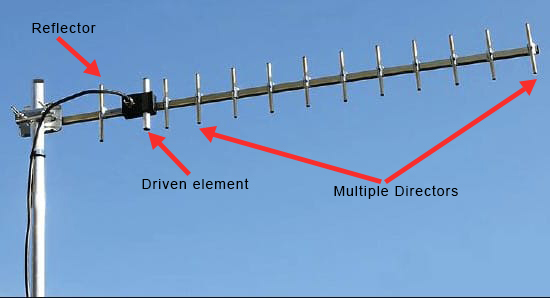
The Yagi-Uda antenna consists of the following key components:
- Driven Element: This is the active element of the antenna, typically a dipole, where the RF signal is applied or received. It is responsible for converting electrical energy into radio waves and vice versa.
- Reflector: Positioned behind the driven element, the reflector is slightly longer than the driven element. Its function is to reflect the signal back toward the driven element, thus boosting the signal in the forward direction.
- Directors: Several director elements, shorter than the driven element, are positioned in front of the driven element. These directors focus the energy forward, increasing the gain and directivity of the antenna.
- Boom: The boom is the supporting structure that holds the elements in place along a common axis. It provides stability without affecting the radiation pattern.
Benefits of Yagi Antennas
Yagi antennas offer several advantages that make them popular in various applications, particularly in areas requiring targeted signal transmission and reception:
- High Gain: Yagi antennas provide high gain, meaning they can focus the signal strength in a specific direction. This makes them highly effective for long-distance communication, such as in television reception and ham radio.
- Directional Focus: The directional Yagi antenna focuses its signal in a single direction, minimizing interference from unwanted directions. This capability enhances communication reliability in areas with a lot of signal congestion.
- Compact Size: Despite their high gain, Yagi antennas are relatively compact, especially when compared to other high-gain antenna types like parabolic dishes. This makes them easier to install and maintain.
- Cost-Effective: Yagi antennas are affordable due to their simple design and relatively low manufacturing cost. Their combination of high performance and affordability makes them a preferred choice for both professional and amateur radio operators.
- Ease of Installation: Yagi antennas are easy to install, especially in outdoor environments. Their simple structure requires minimal setup time, making them a convenient option for various applications.
Applications of Yagi Antennas
Yagi antennas are widely used in many industries due to their versatility and directional capabilities. Some of the most common applications include:
- Television Reception: In rural or remote areas, Yagi antennas are often used to receive over-the-air television signals. Their high gain and directivity allow them to capture distant signals that are weak or disrupted by obstacles.
- Ham Radio: Amateur radio enthusiasts frequently use Yagi antennas for long-distance communication. The directional nature of the antenna helps in reducing interference, making it easier to establish strong connections with other radio operators.
- Cellular Communication: Directional Yagi antennas are used in cellular base stations to improve signal coverage in specific areas. They help boost signal strength and reduce dropped calls in areas with poor reception.
- Wi-Fi Networks: Yagi antennas are sometimes employed in Wi-Fi networks to extend the range of wireless signals. This is particularly useful in large outdoor areas where regular omnidirectional antennas might not provide sufficient coverage.
- Military and Emergency Services: Yagi antennas are also used in military and emergency communication systems, where reliable, long-range communication is critical. Their ability to focus signals in specific directions ensures that communication remains strong and clear, even in challenging environments.
Yagi-Uda Antenna: A Closer Look
The Yagi-Uda antenna is the full name for the standard Yagi antenna, often used in various applications due to its ability to focus energy effectively. It uses a combination of the driven element, reflector, and director elements to create a highly directional radiation pattern. The Yagi-Uda antenna is particularly useful in VHF (Very High Frequency) and UHF (Ultra High Frequency) bands, making it a popular choice for television reception, amateur radio, and other communication systems.
Choosing the Right Yagi Antenna
When selecting a Yagi antenna for a specific application, consider the following factors:
- Frequency Range: Different Yagi antennas are designed for different frequency ranges. Ensure the antenna you select covers the frequency band required for your application, whether it’s VHF, UHF, or another frequency range.
- Gain Requirements: The gain of the Yagi antenna determines how much signal strength it can focus in a particular direction. For long-distance communication, a higher-gain antenna may be necessary.
- Number of Elements: The number of elements (reflector, directors) on the Yagi antenna affects its performance. More elements typically result in higher gain and better directionality, but it can also increase the size of the antenna.
- Environmental Considerations: If you’re installing the Yagi antenna outdoors, consider factors such as wind load, weather resistance, and the durability of materials. Ensure the antenna is built to withstand the environmental conditions in which it will operate.
- Cost: While Yagi antennas are generally cost-effective, the price can vary based on the antenna’s size, gain, and the materials used in its construction. Evaluate your budget and performance needs to choose an antenna that offers the best value.
Conclusion
The Yagi antenna, with its directional capabilities and high gain, remains a critical tool in various communication systems. From television reception to ham radio, Yagi-Uda antennas are known for their ability to provide focused signal transmission over long distances. Whether for personal or professional use, directional Yagi antennas offer a practical, cost-effective solution for enhancing signal quality and coverage.